Knowing how to make payments and manage money beforehand can make traveling easier for foreign tourists. This article provides an overview of Japanese currency, methods of currency exchange, and payment options. While credit cards and mobile payments are widely accepted in urban areas, cash is often essential in rural areas, so be sure to read on for useful tips!
Japanese Currency
The currency in Japan is the yen (¥). Both banknotes and coins are used, and come in the following denominations:
Banknotes
Currently, there are four types of banknotes in circulation:
- 10,000-yen note: The highest denomination.


- 5,000-yen note: A medium denomination, convenient for restaurants or small purchases.


- 2,000-yen note: A rare banknote with limited circulation.


- 1,000-yen note: The most commonly used note, accepted by vending machines.


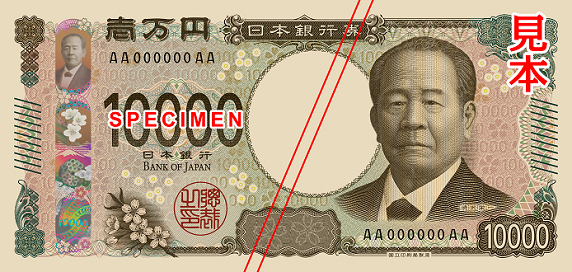
★New Banknotes Released★
On July 3, 2024, Japan introduced new banknote designs for the first time in about 20 years. These new notes (10,000 yen, 5,000 yen, and 1,000 yen) feature modern designs and enhanced anti-counterfeiting technology.
Figures on the New Banknotes
- 10,000 yen: Eiichi Shibusawa, known as “the father of modern Japanese economy.”

- 5,000 yen: Umeko Tsuda, founder of Tsuda University.


- 1,000 yen: Shibasaburo Kitasato, a microbiologist known as “the father of modern Japanese medicine.”
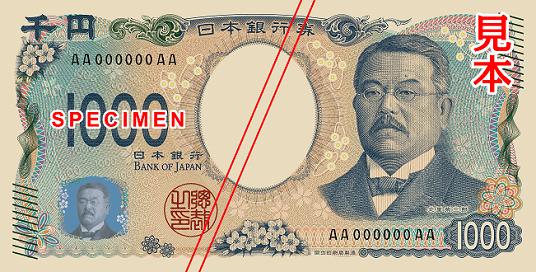
If you come across the new banknotes, take a closer look—they’re fascinating!
Caution!!
Beware of scams claiming that “old banknotes are no longer valid and need to be exchanged.” The older notes remain valid and can still be used alongside the new ones.
Coins
There are six denominations of coins: ¥500, ¥100, ¥50, ¥10, ¥5, and ¥1. They differ in size and material, and while it may take time to get used to them, they are handy once you do.












※The above currency image is sourced from the Ministry of Finance website.
Currency Exchange Methods
Some travelers may already have Japanese yen before arriving in Japan, but here are some convenient ways to obtain yen once you’re here:
At the Airport
Currency exchange counters at airports are a reliable choice upon arrival. They usually have long hours and offer safe service, though their fees may be slightly higher.
Exchange Offices in Stations or Shopping Districts
Major stations and urban areas have currency exchange offices. Many offer multilingual services, with information in English, Chinese, and more.
ATM Cash Withdrawal
If you are using an international debit or credit card, you can withdraw yen from ATMs in Japan. ATMs at 7-Eleven stores and post offices are especially foreigner-friendly, often available 24/7.
Payment Methods: Cash and Cashless
Cashless Payments in Urban Areas
In major cities like Tokyo and Osaka, credit cards are widely accepted. Visa and Mastercard are the most commonly supported brands. Additionally, many stores, tourist attractions, and restaurants frequented by foreign tourists accept mobile payment services like:
- Apple Pay
- Alipay(支付宝)
- WeChat Pay(微信支付)
Cash is Essential in Rural Areas
On the other hand, cash is still the king in many rural areas. Small restaurants, souvenir shops, and public transportation like local buses often only accept cash. To avoid inconvenience during your travels, it is a good idea to carry extra cash.
Summary
A balanced approach to using both cash and cashless payment methods is recommended for traveling in Japan. Credit cards and mobile payments are convenient in urban areas, but cash is indispensable in rural regions and specific situations. Make the most of currency exchange and ATM services, and enjoy a smooth and enjoyable trip to Japan!